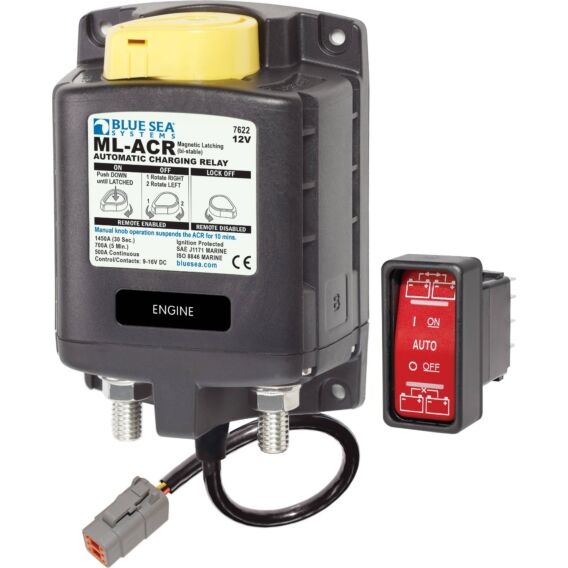
500 Amp magnetic latching (bi-stable) relay automatically combines batteries during charging and isolates batteries when discharging and when starting the engine
- Manual control switch provides an added level of safety allowing control with or without power and offering LOCK OFF capability for servicing
- Automatically manages the charging of two large battery banks
- Allows paralleling of battery banks for emergency starting
- 500 Ampere continuous rating to support high-output alternators
- Magnetic Latch (ML)—ACR draws very low current (<40mA to monitor terminal voltage) in the "ON" or "OFF" states, and draws moderate current for a very short time when changing state
- Dual sensing—senses charge on both battery banks
- Start Isolation (SI)—can be configured for temporary isolation of House loads from Engine circuit during engine cranking to protect sensitive electronics
- Engine Isolation (EI)—can be configured for isolation of two engines while both are running to protect engine electronics and maximize alternator output
- Senses charging on two battery banks
- LED output to remotely indicate when batteries are combined, isolated, in voltage lockout, or in Start or Engine isolation
- 3/8"-16 tin-plated copper studs for maximum conductivity and corrosion resistance
- 7/8" (22mm) stud length accepts multiple cable terminals
- Silver alloy contacts provide high reliability for switching live loads
- Label recesses for circuit identification
| Specifications | |
|---|---|
| Control Circuit Connection | Deutsch DTM* |
| Nominal Voltage | 12V DC |
| Manual Control** | Yes |
| Engine Isolation*** | Yes |
| Mounting | #10 |
| Start Assist**** | Yes |
| Start Isolation***** | Yes |
| Amperage Operating Current | 13mA****** |
| Amperage Operating Current when changing state | <7.0A |
| Terminal Stud Torque | 140 in-lb (15.82 Nm) |
| Continuous Rating******* | 500A |
| Intermittent Rating******** | 700A (5 min) |
| Cranking Rating 30 sec********* | 1450A DC |
| Cable Size to Meet Ratings | 4/0 AWG x 2 |
| Live Current Switching | 300A @ 12V DC |
| Switching Cycles | 100000 |
| Terminal Ring Diameter Clearance | 1.18in (29.97 mm) |
| Terminal Stud Length | 1.50in (38.1 mm) |
| Terminal Stud Size | 3/8" - 16 (M10) |
| Relay Contact Position | |
| Combine 30 sec | 13.5V |
| Combine 90 sec | 13.0V |
| Open 10 sec | 12.35V |
| Open 30 sec | 12.75V |
| Open High | 16.2V |
*Provided on bulk units
**Manual control switch provides an added level of safety allowing control with or without power and offering LOCK OFF capability for servicing
***Condition: Two engines are running
- One relay is open and one relay is closed
- Engine 1 Start and Engine 2 Start batteries are isolated to protect engine electronics
****Condition: Engine starting
- Relay is closed combining batteries
- Batteries are combined to share power in the event of a low start battery
*****Condition: Engine starting
- Relay is open isolating batteries
- Batteries are isolated to protect sensitive electronics from voltage sags and spikes
******@ 25°C nominal VDC
*******The maximum current a switch is designed to conduct for an indefinite period
********The maximum amount of current a switch is designed to carry for a minimum of a designated period of time
*********Normally associated with 'cranking current' which is the current required by the starter circuit prior to engine starting. The cranking current varies significantly during the starting cycle. Initially, there is a large surge of current required to overcome the inertia and compression of the engine. This surge can be two to four times the average cranking current. Once the engine is turning there are peaks and valleys as the pistons go through the compression and exhaust cycles. The cranking current rating is used for sizing batteries, cables, and battery switches